backscattering怎么读,backscattering的音标和真人发音
英音
[bæks'kætərɪŋ]
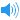



美音 [bæks'kætərɪŋ]




backscattering是什么意思,backscattering的意思是
n.反(向)散射,后向散射
backscattering 的用法和双语例句“点击”或“选中”例句中的单词,就可以看到词义解释
- A sensor on the aircraft records the time it takes to receive the backscattering of pulses , and that is used to compute distances to the forest canopy and to the soil beneath .
- 这架飞机上的一个探测设备记录下它收到脉冲反向散射所需时间而且这个时间可用于计算到森林树冠层和到树冠层下土壤的距离。
- During a forest survey , an aircraft-borne lidar sweeps a beam that fires about 70000 pulses a second over the canopy . A sensor on the aircraft records the time it takes to receive the backscattering of pulses , and that is used to compute distances to the forest canopy and to the soil beneath .
- 在森林探测过程中,载有激光雷达的飞机将每秒产生7万个脉冲的激光束向森林树冠进行扫掠,同时安装在飞机上的探测设备会记录收到脉冲反向散射波的时间,然后分别用于计算到树林冠部及到土壤的距离。
- Airborne laser bathymetry backscattering lidar equation .
- 机载激光测深后向散射光雷达方程。
- Vegetation canopy is one of the important reasons affecting the sensitivity of radar backscattering to soil moisture .
- 地表植被覆盖是影响雷达遥感估算土壤水分的主要因素之一。
- Simulated waste glass corrosion in humic acid solution using rutherford backscattering spectrometry .
- 用卢瑟福反散射光谱测定法模拟废物玻璃在腐殖质酸溶液中的腐蚀。
- Studying nuclear physics on the quark and gluon level using shanghai laser electron backscattering gamma source .
- 用上海的激光-电子散射光源在夸克和胶子层次上研究核物理。
backscattering相邻词汇
热门英文查询
