stator怎么读,stator的音标和真人发音
英音
['steɪtə]
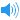



美音 ['steɪtə]




stator是什么意思,stator的意思是
n.定子,固定片
星级词汇:


stator 的用法和双语例句“点击”或“选中”例句中的单词,就可以看到词义解释
- A normal motor ( one that runs on direct current , at least ) has two parts . One , the rotor , moves . The other , the stator , does not .
- 一台正常的电动机(至少是直流电动机)由转动的转子和不动的定子两部分组成。
- Its primary windings reside in a stationary steel casing ( the stator ) and and secondary conductors are attached to an inner shaft ( the rotor ) .
- 其主绕组固定在静止的铁模中(定子)而次级导体被镶在里面的轴承上(转子)。
- In a synchronous motor , the stator 's rotating magnetic field imposes an electromagnetic torque directly on the fixed magnetic field of the rotor , causing the latter assembly to spin on its axis in sync with the stator field .
- 在同步发动机机中,定子的旋转磁场往转子的固定磁场施加电磁转矩,导致后者集体与定子磁场同步轴旋转。
- With an alternating current now circulating within it , the rotor creates a rotating magnetic field of its own , which proceeds to chase the stator 's rotating field-causing the rotor to spin in the process and generate torque .
- 随着交流电在转子内部流通,转子形成了自己的一个旋转磁场,这个磁场继续追逐定子的旋转磁场,使得转子在过程中产生扭转力。
- As he explained , axial flux motors are different from conventional electric motors because the path of its magnetic flux flows parallel to the axle of the motor . In a conventional motor this flux flows radiallly though a gap between the rotor and stator .
- 根据他的解释,轴向磁通电机与普通的电机不同,是因为它的磁通量的方向跟电机的轴是平衡的,在一个普通电机里,这些磁通量是放射状地通过一个在转子和定子之间的一个间隔的。
- The stator usually forms the casing and houses a set of permanent magnets .
- 定子通常组成外壳,内部装有一组永久磁铁。
- Such machines are known as asynchronous motors , because the rotor 's magnetic field never catches up with the stator 's field .
- 这样的设备被称为异步电动机,因为转子的磁场总是滞后于定子的磁场。
- Modern induction motors usually have three ( or more ) sets of stator windings , each using a different phase of the alternating current being applied .
- 现代的感应电动机通常具有三组(或者更多)的定子绕组,每组各自使用不同相位的交流电来驱动。
- An alternating current applied to the stator 's windings creates a rotating magnetic field , while simultaneously inducing a current in the separate conductors attached to the rotor .
- 交流电通过定子线圈创造旋转磁场,导致镶在转子上的独立导体同时产生感应电流。
热门英文查询
